
(in other words we reduced 100% to decimal form 1. Contrast this with the atomic number, which is simply the number of protons. N is a constant called Avogadros number and its equal to 6.0221023 atoms/mole.

Calculating the Relative Atomic Mass of an Element. Mass number is often denoted using a capital letter A. of atoms N (density) volume / (Molecular Weight). The mass number ,A, is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. In other words, it is the sum of the number of nucleons in an atom. This calculation gives us the mass of a single atom of an.

A comparable calculation for an atom shows that the atomic binding energy is. But we can figure it out by adding up the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
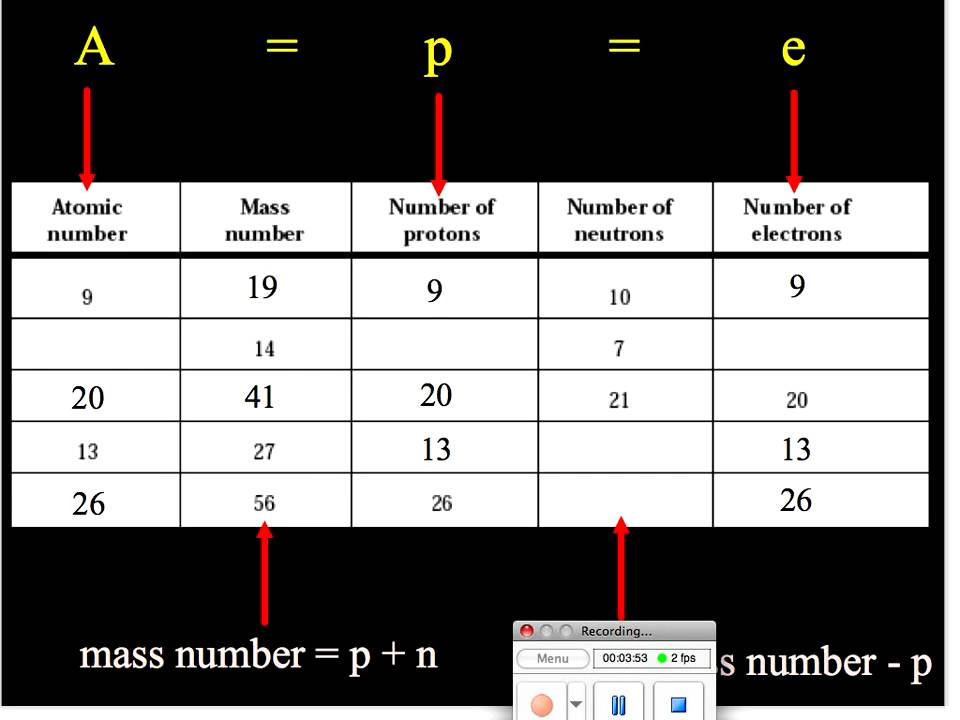
We will let 6Li = x and 7 Li = 1-x we use 1 – x instead of 100 – x because the small number is easier to work with. Mass number is an integer (whole number) equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atomic nucleus. For any nucleus of atomic and mass numbers Z and A, the (positive amount. Since I don’t know what the percentage are, I will have to use variables.ġ00% of Lithium is determined by these two naturally occurring isotopes. Determine the percent abundance of each isotope.Īw = + + Ħ.94 = + The atomic mass of lithium is 6.94, the naturally occurring isotopes are 6Li = 6.015121 amu, and 7Li = 7.016003 amu. What are the percent abundances of the isotopes? Since the overall atomic weight for copper is not given in the problem, you must look it up in the periodic table to work this solution. If you look in the periodic table you will be able to check that our answer is correct!ģVerify that the atomic mass of magnesium is 24.31, given the followingĪtomic mass= + + ĭetermining the percent abundance of each isotope from atomic mass.Ĭopper exists as two isotopes: 63Cu (62.9298 amu) and 65Cu (64.9278 amu). The mass number is the sum of number of protons and number of neutrons present in side the nucleus of the atom. An atomic weight (relative atomic mass) of an element from a specified source is the ratio of the average mass per atom of the element to 1/12 of the mass of. 10.81amu so, the atomic weight of B = 10.81amu A hydrogen atom has one proton but no neutrons. Similarly, because a carbon atom contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons, its mass number is 6+612. One atom of sodium, for example, contains 12 neutrons and 11 protons, therefore the mass number of sodium is 11+1223. When an organism dies, it stops taking in carbon-14, so the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in its remains, such as fossilized bones, will decline as carbon-14 decays gradually to nitrogen-14 2 ^2 2 squared. Mass number Number of protons + Number of neutrons.

The following is the calculation of the atomic pass of hydrogen. As animals eat the plants, or eat other animals that ate plants, the concentrations of carbon-14 in their bodies will also match the atmospheric concentration. The masses of the isotopes and the percent abundances are used to calculate the atomic mass that is reported on the periodic table. As plants pull carbon dioxide from the air to make sugars, the relative amount of carbon-14 in their tissues will be equal to the concentration of carbon-14 in the atmosphere. The atomic mass of atoms, ions, or atomic nuclei is slightly less than the sum of the masses of their constituent protons, neutrons, and electrons, due to binding energy mass loss (per E mc2 ). These forms of carbon are found in the atmosphere in relatively constant proportions, with carbon-12 as the major form at about 99%, carbon-13 as a minor form at about 1%, and carbon-14 present only in tiny amounts 1 ^1 1 start superscript, 1, end superscript. In general, the molecular mass, molecular weight, molar mass, or formula weight of a chemical compound can be used when using a molarity or concentration. For example, carbon is normally present in the atmosphere in the form of gases like carbon dioxide, and it exists in three isotopic forms: carbon-12 and carbon-13, which are stable, and carbon-14, which is radioactive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
